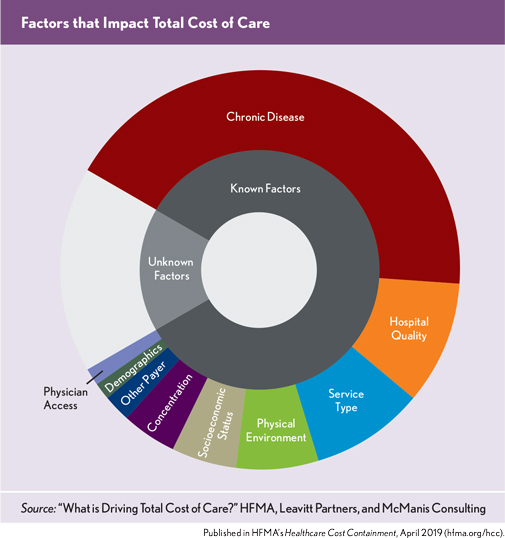
The prevalence of chronic diseases was the most significant factor in total cost of care variations across U.S. healthcare markets, according to What is Driving Total Cost of Care?” a study by HFMA, Leavitt Partners, and McManis Consulting. Combined, the factors identified predicted 82 percent of the variation in baseline costs.
These factors proved much less successful, however, in predicting variations in growth in total cost of care. Combined, they predicted just 27 percent of variation in growth. The significance of factors also shifted, with physical environment factors (such as average daily temperatures) predicting more of the variation in cost growth than prevalence of chronic diseases.
The quantitative analysis also indicated that, although health plan and hospital concentration had a statistically significant impact on predicting baseline total cost of care and growth in costs, the impact was relatively marginal compared with other factors and could have both positive negative and positive impacts on cost.
For more information, read the study at hfma.org/tcoc.





